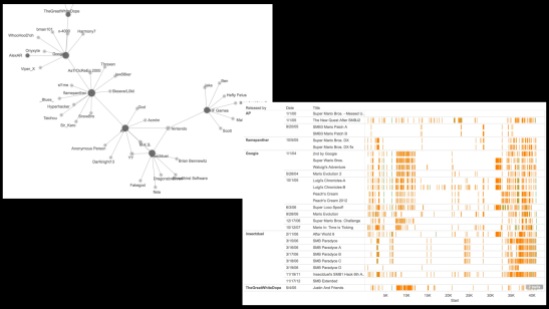
Here’s a sneak peek at something I’ve been working on for a jointly authored piece with Andreas Jahn-Sudmann (more details soon!):
[…] whereas the relatively recent example of bullet time emphasizes the incredible speed of our contemporary technical infrastructure, which threatens at every moment to outstrip our phenomenal capacities, earlier examples often mediated something of an inverse experience: a mismatch between the futurist fantasy and the much slower pace necessitated by the techno-material realities of the day.
The example of Super Star Trek (1978) illuminates this inverse sort of experience and casts a media-archaeological light on collective serialization, by way of the early history of gaming communities and their initially halting articulation into proto-transmedia worlds. Super Star Trek was not the first – and far from the last – computer game to be based on the Star Trek media franchise (which encompasses the canonical TV series and films, along with their spin-offs in comics, novels, board games, role-playing games, and the larger Trekkie subculture). Wikipedia lists over seventy-five Trek-themed commercial computer, console, and arcade games since 1971 (“History of Star Trek Games”) – and the list is almost surely incomplete. Nevertheless, Super Star Trek played a special role in the home computing revolution, as its source code’s inclusion in the 1978 edition of David Ahl’s BASIC Computer Games was instrumental in making that book the first million-selling computer book.[i] The game would continue to exert a strong influence: it would go on to be packaged with new IBM PCs as part of the included GW-BASIC distribution, and it inspired countless ports, clones, and spin-offs in the 1980s and beyond.
A quick look at the game’s source code reveals that Super Star Trek didn’t just come out of nowhere, however: Here, the opening comment lines (“REM” indicates a non-executable “remark” in BASIC) mention not only the “Star Trek TV show” as an influence, but also a serial trajectory of inter-ludic programming, modification, debugging, and conversion (porting) that begins to outline a serialized collectivity of sorts. Beyond those participants mentioned by name (Mike Mayfield, David Ahl, Bob Leedom, and John Borders), a diffuse community is invoked – “with a little help from his friends…” – and, in fact, solicited: “comments, epithets, and suggestions” are to be sent personally to R. C. Leedom at Westinghouse Defense & Electronics. Reminiscent of a comic-book series’ “letters to the editor” page (cf. Kelleter and Stein 2012), this invitation promises, in conjunction with the listing of the game’s serial lineage, that readers’ opinions are valued, and that significant contributions will be rewarded (or at least honored with a hat-tip in the REM’s). Indeed, in these few preliminary lines, the program demonstrates its common ground with serialized production forms across media: since the nineteenth century, readers have written to the authors of ongoing series in order to praise or condemn – and ultimately to influence – the course of serial unfolding (cf. Hayward 1997, Looby 2004, Smith 1995, Thiesse 1980); authors dependent on the demands of a commercial marketplace were not at liberty simply to disregard their audience’s wishes, even if they were free to filter and select from among them. What we see, then, from an actor-network perspective, is that popular series therefore operate to create feedback loops in which authors and readers alike are involved in the production of serial forms (cf. Kelleter 2012a) – which therefore organize themselves as self-observing systems around which serialized forms of (para-)social interaction coalesce (cf. Kelleter 2012d, as well as the contributions to Kelleter 2012b).
The snippet of code above thus attests to the aspirations of a germinal community of hackers and gamers, which has tellingly chosen to align itself, in this case, with one of the most significant and quickly growing popular-culture fan communities of the time: viz. the Trekkie subculture, which can be seen to constitute a paradigmatic “seriality” in Anderson’s sense – a nation-like collective (complete with its own language) organized around the serialized consumption of serially structured media. And, indeed, the computing/gaming community had its own serialized media (and languages) through which it networked, including a plethora of computer-listings newsletters and magazines – such as David Ahl’s Creative Computing, where Super Star Trek had been published in 1974, before BASIC Computer Games made it more widely known; or People’s Computer Company, where Bob Leedom had mentioned his version before that; or the newsletter of the Digital Equipment Computer User Society, where Ahl had originally published a modified version of Mike Mayfield’s program. These publications served purposes very much like the comic-book and fanzine-type organs of other communities; here, however, it was code that was being published and discussed, thus serving as a platform for further involvement, tweaking, and feedback by countless others. Accordingly, behind the relatively linear story of development told in the REM’s above, there was actually a sprawling, non-linear form of para-ludic serialization at work in the development of Super Star Trek.[ii]
And yet we see something else here as well: despite the computing industry’s undeniable success in moving beyond specialized circles and involving ever larger groups of people in the activity of computing in the 1970s (and gaming must certainly be seen as central to achieving this success), the community described above was still operating with relatively crude means of collective serialization – more or less the same paper-bound forms of circulation that had served the textual and para-textual production of popular serialities since the nineteenth century. In many ways, this seems radically out of step with the space-age fantasy embodied in Super Star Trek: in order to play the game, one had to go through the painstaking (and mistake-prone) process of keying in the code by hand. If, afterwards, the program failed to run, the user would have to search for a misspelled command, a missing line, or some other bug in the system. And God forbid there was an error in the listing from which one was copying! Moreover, early versions of the game were designed for mainframe and minicomputers that, in many cases, were lacking a video terminal. The process of programming the game – or playing it, for that matter – was thus a slow process made even slower by interactions with punch-card interfaces. How, under these conditions, could one imagine oneself at the helm of the USS Enterprise? There was a mismatch, in other words, between the fantasy and the reality of early 1970s-era computing. But this discrepancy, with its own temporal and affective dynamics, was a framing condition for a form of collective serialization organized along very different lines from contemporary dreams of games’ seamless integration into transmedia worlds.
To begin with, it is quite significant that Super Star Trek’s functional equivalent of the “letters to the editor” page, where the ongoing serialization of the game is both documented and continued, is not printed in an instruction manual or other accompanying paraphernalia but embedded in the code itself. In contrast to the mostly invisible code executed in mainstream games today, Super Star Trek’s code was regarded as highly visible, the place where early gamers were most likely to read the solicitation to participate in a collective effort of development. Clearly, this is because they would have to read (and re-write) the code if they wished to play the game – while their success in actually getting it to work were more doubtful. Gameplay is here subordinated to coding, while the pleasures of both alike were those of an operational aesthetic: whether coding the game or playing it, mastery and control over the machine were at stake. Unlike the bullet time of The Matrix or Max Payne, which responds to an environment in which gamers (and others) are hard-pressed to keep up with the speed of computation, Super Star Trek speaks to a somewhat quainter, more humanistic dream of getting a computational (or intergalactic) jalopy up and running in the first place. In terms of temporal affectivities, patience is tested more so than quick reactions. If bullet time slowed down screen events while continuing to poll input devices as a means for players to cope with high-velocity challenges, the tasks of coding and playing Super Star Trek turn this situation around: it is not the computer but the human user who waits for – hopes for – a response. As a corollary, however, relatively quick progress was observable in the game’s inter-ludic development, which responded to rapid innovations in hardware and programming languages. This fact, which corresponded well with the basically humanistic optimism of the Star Trek fantasy (as opposed to the basically inhuman scenario of The Matrix), motivated further involvement in the series of inter-ludic developments (programming, modification, debugging, conversion…), which necessarily involved coder/tinkerers in the para-ludic exchanges upon which a gaming community was being built. […]
[ii] A better sense of this can be had by taking a look at all the various iterations of the game – encompassing versions for a variety of flavors of BASIC and other languages as well – collected by Pete Turnbull (http://www.dunnington.u-net.com/public/startrek/).
Hayward, J. (1997) Consuming Pleasures: Active Audiences and Serial Fictions from Dickens to Soap Opera. Lexington: UP of Kentucky.
Kelleter, F. (2012a) Populäre Serialität: Eine Einführung. In Kelleter F., ed. Populäre Serialität: Narration – Evolution – Distinktion. Zum seriellen Erzählen seit dem 19. Jahrhundert. Bielefeld: Transcript, pp. 11-46.
Kelleter, F., ed. (2012b) Populäre Serialität: Narration – Evolution – Distinktion. Zum seriellen Erzählen seit dem 19. Jahrhundert. Bielefeld: Transcript.
Kelleter, F. (2012d) The Wire and Its Readers. In Kennedy, L. and Shapiro, S., eds. “The Wire”: Race, Class, and Genre. Ann Arbor: U of Michigan P, pp. 33-70.
Kelleter, F. and Stein, D. (2012) Autorisierungspraktiken seriellen Erzählens: Zur Gattungsentwicklung von Superheldencomics. In Kelleter, F., ed. Populäre Serialität: Narration – Evolution – Distinktion. Zum seriellen Erzählen seit dem 19. Jahrhundert. Bielefeld: Transcript, pp. 259-290.
Looby, C. (2004) Southworth and Seriality: The Hidden Hand in the New York Ledger. Nineteenth-Century Literature 59.2, pp. 179-211.
Smith, S. B. (1995) Serialization and the Nature of Uncle Tom’s Cabin. In Price, K. M. and Smith, S. B., eds. Periodical Literature in Nineteenth-Century America. Charlottesville: UP of Virginia, pp. 69-89.
Thiesse, A.-M. (1980) L’education sociale d’un romancier: le cas d’Eugène Sue. Actes de la recherche en sciences sociales 32-33, pp. 51-63.