On January 30, 2015 (12:00-1:00pm), I will be speaking about visualization techniques and game-related serialization processes at the Duke Visualization Friday Forum. Organized by Eric Monson and Angela Zoss, this is a very exciting and robustly interdisciplinary venue, as the long list of sponsors for the weekly forum indicates: Information Science + Information Studies, the Duke immersive Virtual Environment (or DiVE), Media Arts + Sciences, Data and Visualization Services, the Department of Computer Science, Research Computing at the Office of Information Technology, and Visualization & Interactive Systems.
As this list indicates, the Visualization Friday Forum has the potential to take just about anyone — but especially humanities-types like me — out of their comfort zone; but it does so in the most comfortable way possible: the informal setting of a lunchtime chat fosters a type of exchange that is interdisciplinary in the best sense. Artists, computer scientists, media scholars, digital humanists, historians, literary critics, mathematicians, and researchers in the natural sciences, among others, make a genuine effort to understand one another. And, to judge from the times I have been present or watched a live-stream of the Forum, this effort is usually quite successful.
So here’s hoping that my own effort at interdisciplinary dialogue will be as successful! In my talk, I will discuss an ongoing project, some preliminary findings of which I posted not too long ago. Here’s the abstract:
Visualizing Digital Seriality: Correlating Code and Community in the Super Mario Modding Scene
Shane Denson (DAAD Postdoctoral Fellow, Duke Literature)
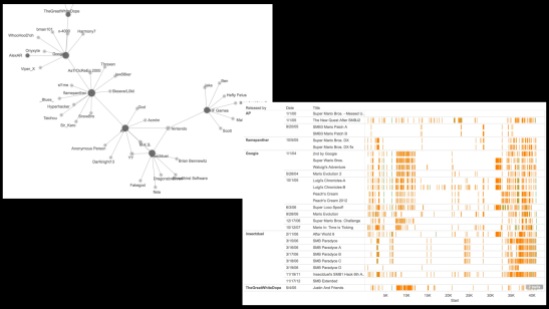
Seriality is a common feature of game franchises, with their various sequels, spin-offs, and other forms of continuation; such serialization informs social processes of community-building among fans, while it also takes place at much lower levels in the repetition and variation that characterizes a series of game levels, for example, or in the modularized and recycled code of game engines. This presentation considers how tools and methods of digital humanities – including “distant reading” and visualization techniques – can shed light on serialization processes in digital games and gaming communities. The vibrant “modding” scene that has arisen around the classic Nintendo game Super Mario Bros. (1985) serves as a case study. Automated “reading” techniques allow us to survey a large collection of fan-based game modifications, while visualization software such as Tableau and Palladio help to bridge the gap between code and community, revealing otherwise invisible connections and patterns of seriality.